The Covid-19 pandemic has produced major changes in all areas of life, introducing new professional, social and personal scenarios. And if people and their patterns and behaviour change, cities will inevitably change too.
The cities of the future will therefore be more digital, ecological and inclusive, as emerges from the data of the EY Human Smart City Index, an annual survey that identifies trends in the evolution of cities and that, starting this year, also integrates indicators related to ecological behaviour, citizens’ digital skills and social inclusion, arriving at a total of 456 indicators.
By cross-referencing data related to cities’ investments and initiatives, which measure how ready they are to redesign spaces and times around people’s needs (defined as readiness) with citizens’ behaviour on the three strategic axes of ecological transition, digital transition and social inclusion, the ranking is outlined, which puts Italian cities in order according to their transformation process into ‘people-friendly’ cities.
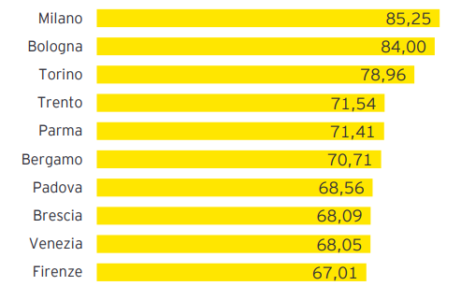
Milan, Bologna and Turin are the three Italian cities on the podium: Milan‘s strong point is said to be linked to digital transition, both in terms of infrastructure (ultra-broadband, 5G and IoT) and the skills of citizens and the use of online services; Bologna follows, thanks to its supremacy in terms of social inclusion; Turin consolidates its presence on the podium thanks to the component linked to citizens’ behaviour, especially in terms of ecological transition.
Here is the top ten:
“In this particular historical context, cities must not only invest in infrastructure and services, but also and above all in listening to citizens and workers. The social component has also become central in the competition between cities for the attraction of companies and talent. New relationships between cities and companies must be reset by keeping people at the centre.” – Andrea D’Acunto, EY People Advisory Services Leader.
Sources: ey.com | pmi.it | smartcitiesindex.org